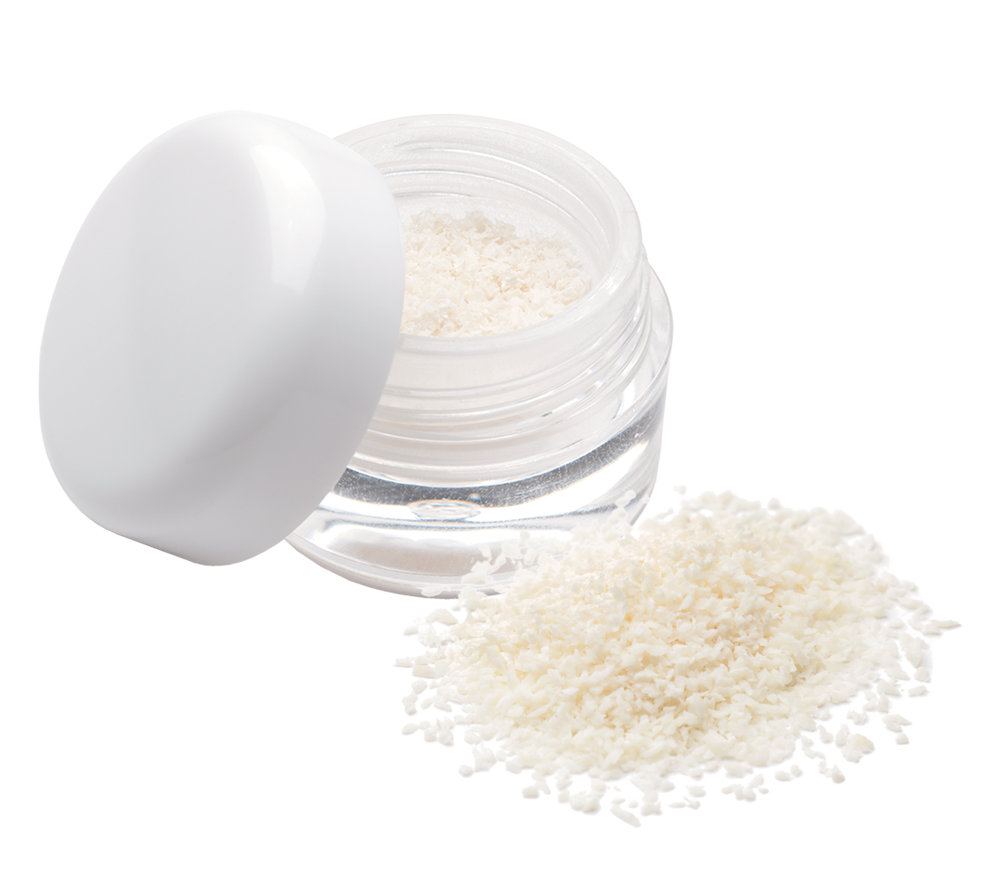
Puros® Cancellous Particulate Allograft
Clinicians around the globe have counted on the Puros family of allografts for hard- and soft-tissue augmentation procedures for years.

Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft with a history of documented clinical results, is an easy-to-handle choice for predictable bone regeneration and acts as an osteoconductive scaffold for new bone formation.1-8
With a history of well-documented clinical results, Puros Cancellous is an easy-to-handle choice for predictable bone reconstruction and acts as an osteoconductive scaffold for new bone formation.1-8
Puros Cancellous Particulate Clinical Evidence
THE POWER OF PUROS® ALLOGRAFTS

- Up to 127% more vital bone formation compared to non-resorbable xenograft in sinus-lift procedures2, 3, 9
- Newly formed vital bone after 3 to 5 months4,8,10 in extraction sockets
- 56% more graft-to-bone contact compared to non-resorbable xenograft 3
- Ø 9.7 mm vertical gain after 4 to 5 months when using Puros Allograft particulate with tenting screws11
- Retains osteoconductive properties due to the preservation of the natural bone matrix collagen and mineral composition, trabecular pattern, and original porosity;1-6, 8, 12-14 enabling the ingrowth of vascular and cellular connective tissue4
Puros Allograft Block Unique Tutoplast Process
In 1969 the Tutoplast Tissue Sterilization Process was developed to sterilize and preserve tissue for implantation. More than 11 million implants have been sterilized through the Tutoplast Process with zero confirmed incidence of implant-associated infection.17
The Benefits of the Multi-Step Tutoplast Process
For allograft bone grafts, the process preserves the valuable bone mineral, collagen matrix, and tissue integrity 18 while inactivating pathogens and gently removing unwanted materials, such as cells, antigens, and viruses 17 – resulting in predictable, reliable, sterile, and safe tissue.17
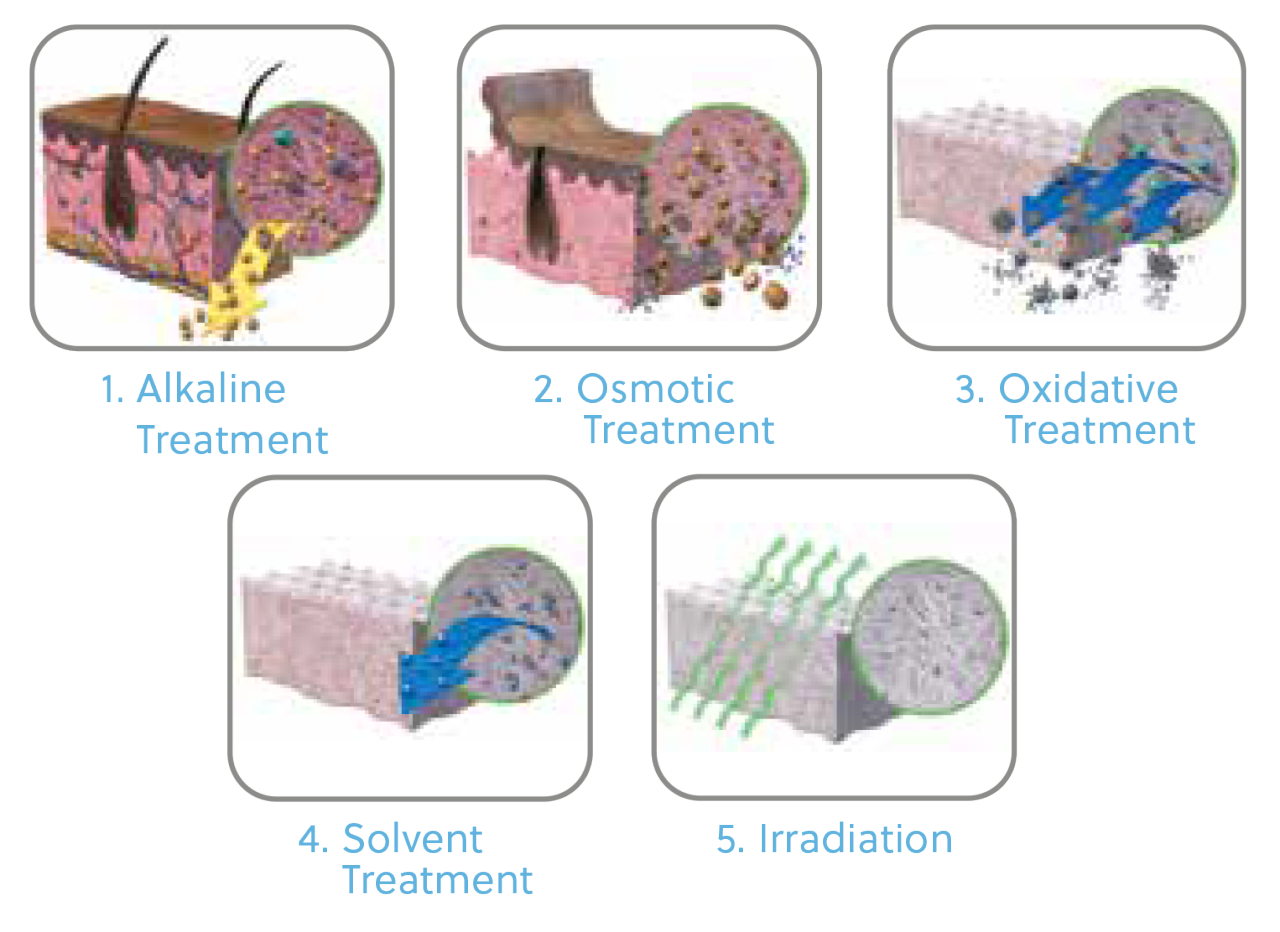
*Images depict dermal processing
Clinically successful in procedures for:
- Repair of periodontal bone and furcation defects1, 6, 15
- Reconstruction of extraction sockets4, 7, 8, 10
- Reconstruction of gaps around block grafts12, 13
- Horizontal and vertical alveolar ridge augmentation16-19
- Sinus augmentation2, 9, 20, 21
